Model-Based Definition (MBD)
![]()
![]()
![]()
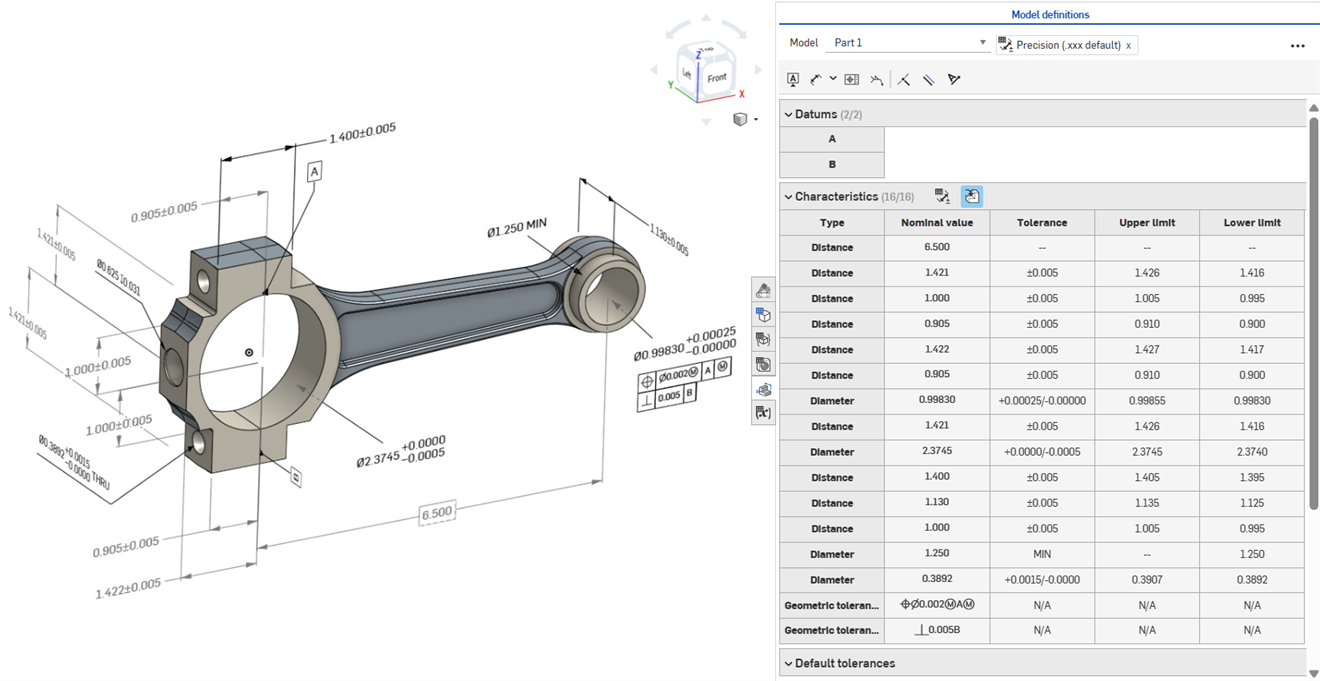
Model-based definition (MBD) refers to the process of dimensioning and annotating the model in the Part Studio so the model contains all the data needed to define a product, With MBD, the model becomes the source authority that drives all engineering activities. This model may further be used downstream by suppliers and across organizations.
MBD data works in conjunction with the Inspection table, where MBD data can be viewed, added, and exported for each part in a Part Studio.
MBD is not intended to replace Drawings. MBD is intended to capture and extend a model's Product manufacturing information (PMI) and Model-based enterprise (MBE) information for additional or alternative downstream usage.
Some features of MBD:
-
Dimension and annotation metadata embedded in the model in the Part Studio.
-
Improve real-time collaboration on the model in the Part Studio.
-
Provide a single source of truth for engineers across the organization.
-
Link to downstream processes like Coordinate measuring machine (CMM) inspection.
Les tolérances définissent la plage de valeurs autorisées pour une cote d'esquisse ou un paramètre de fonction spécifié, tel que la profondeur d'extrusion, l'angle de révolution ou le diamètre du perçage. Les cotes des esquisses ou les paramètres des fonctions ne peuvent pas tous utiliser des tolérances.
Les tolérances sont disponibles dans FeatureScript et peuvent être utilisées dans les fonctions personnalisées. Consultez la section Fonctions personnalisées pour plus d'informations, et reportez-vous à FeatureScript pour de la documentation supplémentaire.
La boîte de dialogue contextuelle Cote permet de modifier les cotes des esquisses et des fonctions et d'ajouter des tolérances. Double-cliquez sur une cote dans une esquisse ou sur une cote MBD dans la zone graphique pour accéder à cette boîte de dialogue. Voir Modifier les cotes MBD.
-
Cliquez sur l'icône de tolérance (
 ) pour ajouter une tolérance à la cote.
) pour ajouter une tolérance à la cote. -
Une fois la tolérance définie, cliquez sur la flèche déroulante (
 ) pour définir les paramètres de tolérance :
) pour définir les paramètres de tolérance :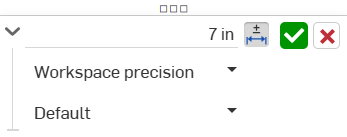
-
Précision - Utilisez la liste déroulante pour sélectionner une unité de précision, soit la précision de l'espace de travail, soit une autre valeur de précision dans la liste déroulante, entre 0 et 6 décimales.
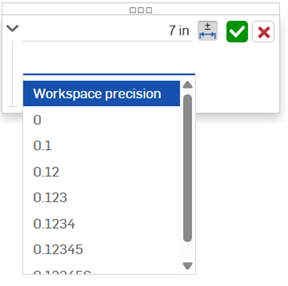
-
Type de tolérance - Sélectionnez un type de tolérance dans la liste déroulante. Les options sont : Par défaut, Aucune tolérance, Symétrique, Déviation, Limites, Min, Max et Basique.
Les tolérances relatives au diamètre des perçages et des esquisses proposent également les options Ajuster, Ajustement avec tolérance et Ajustement (tolérance uniquement). Consultez la section Fonction Perçage pour plus d'informations.
With Default selected, tolerances are based on Default tolerances. See Onshape default tolerances library and Default tolerances library for further information.
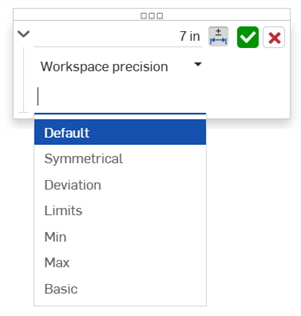
-
Déviation - Disponible pour le type de tolérance Symétrique. Saisissez une valeur de déviation.
-
Supérieur - Disponible pour les types de tolérance Déviation et Limites. Saisissez la valeur de tolérance supérieure.
-
Inférieur - Disponible pour les types de tolérance Déviation et Limites. Saisissez la valeur de tolérance inférieure.
-
Standard - Disponible pour les types de tolérance Ajuster, Ajustement avec tolérance et Ajustement (tolérance uniquement). Sélectionnez la norme ANSI ou ISO dans la liste déroulante.
- Type d'ajustement - Disponible pour les types de tolérance Ajuster, Ajustement avec tolérance et Ajustement (tolérance uniquement). Sélectionnez Défini par l'utilisateur, Dégagement, Transition ou Interférence dans la liste déroulante.
- Classe de perçage - Disponible pour les types de tolérance Ajuster, Ajustement avec tolérance et Ajustement (tolérance uniquement). Sélectionnez une option de classe de perçage dans la liste déroulante.
- Classe d'arbre - Disponible pour les types de tolérance Ajuster, Ajustement avec tolérance et Ajustement (tolérance uniquement). Sélectionnez une classe d’arbre dans la liste déroulante.
-
-
-
Cliquez sur l'icône en forme de coche (
 ) pour accepter les valeurs saisies dans la boîte de dialogue contextuelle.
) pour accepter les valeurs saisies dans la boîte de dialogue contextuelle. -
Cliquez sur l'icône X (
 ) pour quitter la boîte de dialogue contextuelle sans aucune modification.
) pour quitter la boîte de dialogue contextuelle sans aucune modification. -
Cliquez et faites glisser la souris à l'aide de la poignée de la boîte de dialogue (
 ) pour déplacer la boîte de dialogue vers un nouvel emplacement à l'écran. Lâchez la souris pour la placer à son nouvel emplacement.
) pour déplacer la boîte de dialogue vers un nouvel emplacement à l'écran. Lâchez la souris pour la placer à son nouvel emplacement.
Les cotes d'esquisse suivantes peuvent utiliser des tolérances :
-
Distance entre 2 lignes
-
Distance entre deux points
-
Distance entre la géométrie d'esquisse et un plan
-
Distance diagonale
-
Diamètre
-
Angle
-
Distance directe
-
Distance linéaire
-
Rayon
Les cotes d'esquisse suivantes ne peuvent pas utiliser de tolérances :
-
Distance sur une seule ligne
-
Longueur de l'arc
-
Distances à l'axe de symétrie
Consultez la section Cotes d'outil d'esquisse pour en savoir plus.
-
Dessinez l'entité d'esquisse et saisissez les valeurs souhaitées dans les champs de saisie instantanée.
-
Double-cliquez sur la cote (première image ci-dessous). La boîte de dialogue contextuelle Cote s'ouvre (deuxième image ci-dessous) :
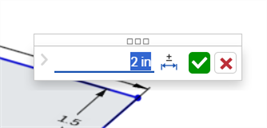
-
To add a tolerance to the dimension, click the Tolerance options icon (
 ; first image below), and then click the dropdown arrow (
; first image below), and then click the dropdown arrow ( ; second image below):
; second image below):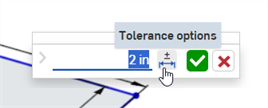
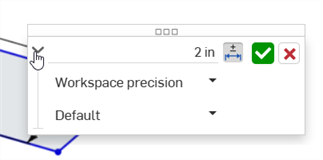
-
Saisissez la précision et le type de tolérance, avec les valeurs spécifiées :
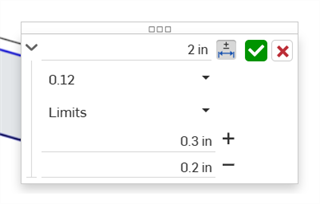
-
Cliquez sur la coche (
 ) pour accepter la cote de l'esquisse.
) pour accepter la cote de l'esquisse.
Les options de fonction suivantes peuvent utiliser des tolérances :
-
Extruder
-
Solide/Surface/Mince - Profondeur
-
Solide/Surface/Mince - Distance de décalage
-
Solide/Surface/Mince - Seconde position d'arrivée - Distance de décalage
-
Mince - Épaisseur 1
-
Mince - Épaisseur 2
-
Mince - Plan milieu - Épaisseur
-
-
Pivoter
-
Solide/Surface/Mince - Une direction/Symétrique/Deux directions - Angle de révolution
-
Thin - Thickness 1
-
Mince - Épaisseur 2
-
Mince - Plan milieu - Épaisseur
-
-
Congé
-
Rayon
-
-
Chanfrein
-
Distance (distance égale)
-
Distance 1, Distance 2 (Deux distances)
-
Distance et angle (Distance, Angle)
-
-
Perçage
-
Diamètre (Simple/Chambrage/Fraisage)
-
Distance (Profondeur - Simple/Chambrage/Fraisage)
-
Diameter (Counterbore/Countersink diameter)
-
Distance (Profondeur du chambrage)
-
Angle (Angle de fraisage)
-
Distance (Tapped depth)
-
Distance (Tap drill diameter)
-
-
Créez une fonction qui accepte une tolérance (Extruder dans cet exemple).
-
Cliquez sur l'icône des options de tolérance (
 ) à droite du paramètre :
) à droite du paramètre :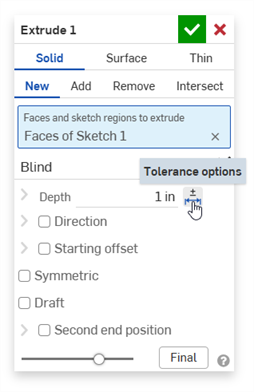
-
Click the dropdown arrow (
 ) to the left of the parameter:
) to the left of the parameter: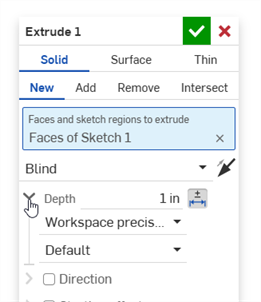
-
Saisissez la précision et le type de tolérance, avec les valeurs spécifiées :
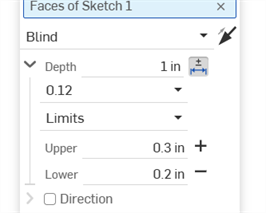
-
Enter any other Feature settings and click the checkmark (
 ) to accept the Feature.
) to accept the Feature. -
Assurez-vous que le Tableau d'inspection (
 ) est ouvert pour voir la valeur de la cote de la fonction avec la tolérance :
) est ouvert pour voir la valeur de la cote de la fonction avec la tolérance :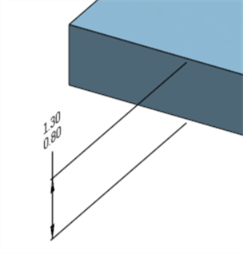
Supprimer la tolérance d'une fonction ne supprime pas la cote du modèle, car c'est toujours une cote valide.
Tolerance options can be used in conjunction with configurations.
-
Click the Tolerance options icon (
 ) to make the configuration's option value tolerant:
) to make the configuration's option value tolerant: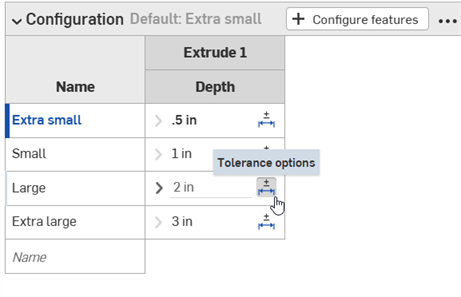
-
Click the dropdown arrow icon (
 ) to the left of the parameter in order to set the tolerance Precision and Type.
) to the left of the parameter in order to set the tolerance Precision and Type.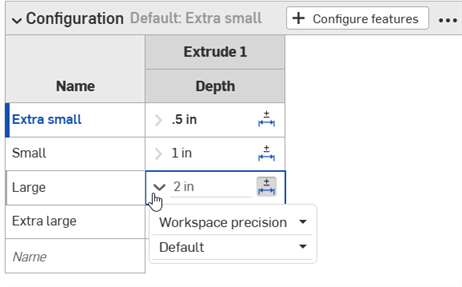
See Configurations for more information.
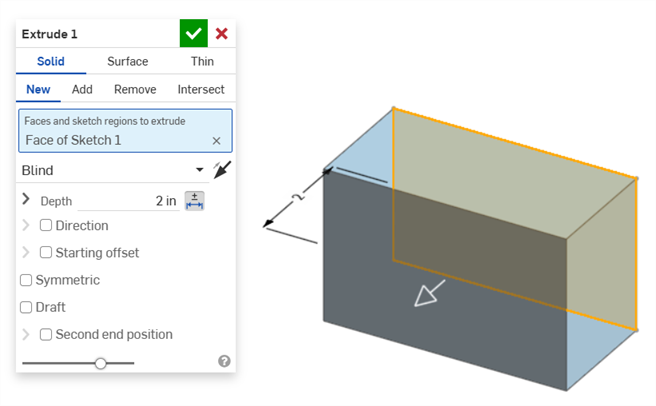
Tolerance options are automatically used in conjunction with the Compare mechanism. When comparing 2 history entries, select the Feature to compare (Extrude 1 in the example below). Comparisons between differing Tolerance options in the entries are outlined in yellow:
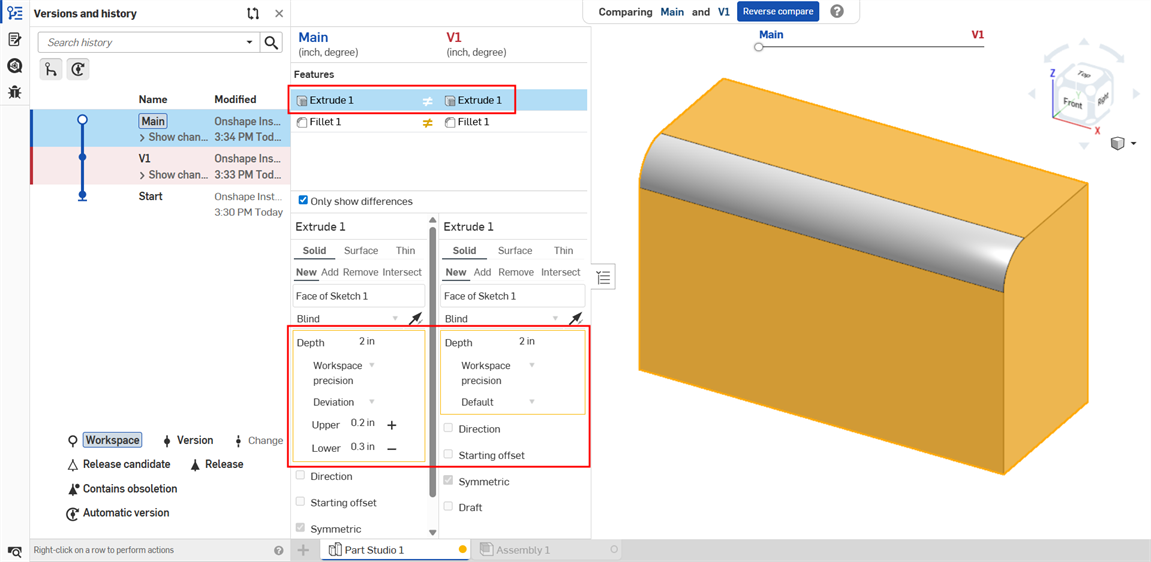
Extrude: Depth tolerance options compared between two history entries
See Compare for more information.
Images below are from iOS. The workflow is the same for both iOS and Android.
Sketch dimension tolerances:
-
Double-tap the dimension on-screen.
-
Click on the Tolerance options button at the lower right corner of the Android Dimension context dialog to set the dimension as tolerant:
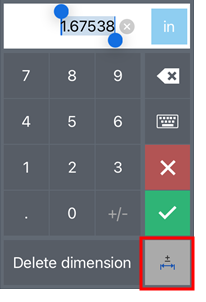
-
In the Tolerance options dialog, enter the Precision and/or Tolerance type and click the checkmark to accept the options:
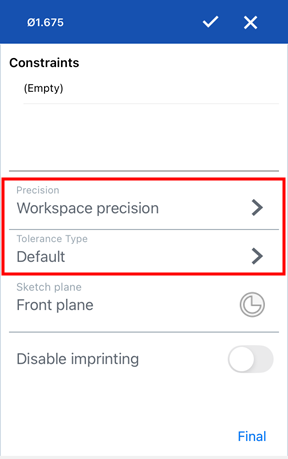
Feature dimension tolerance:
Feature dimensions can be set and edited in the same way as on the desktop platform:
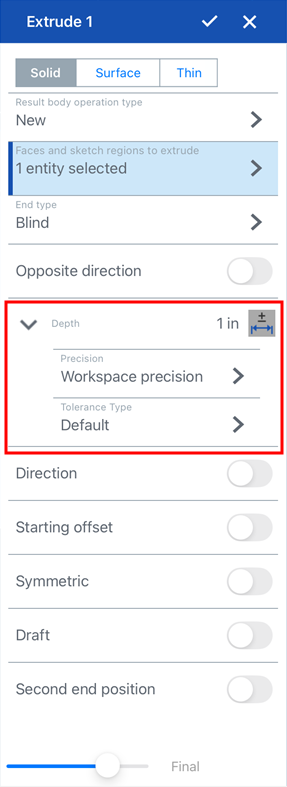
Tolerance options for the Extrude: Depth value
Tolerances can only be viewed on the desktop platform, not iOS or Android, since the Inspection table is available only on desktop.
Currently on iOS and Android you cannot set a tolerance Precision and Type for a Hole feature's Depth parameter if its Termination is Up to Entity or Up to next. Use a Desktop platform to set tolerances for this parameter.
Driving MBD sketch and feature dimensions can be edited directly from the graphics area.
-
Open the Inspection panel (
 ) to display the MBD dimensions in the graphics areas (left image below).
) to display the MBD dimensions in the graphics areas (left image below). -
Double-click on the driving dimension that is associated with a sketch (right image below):
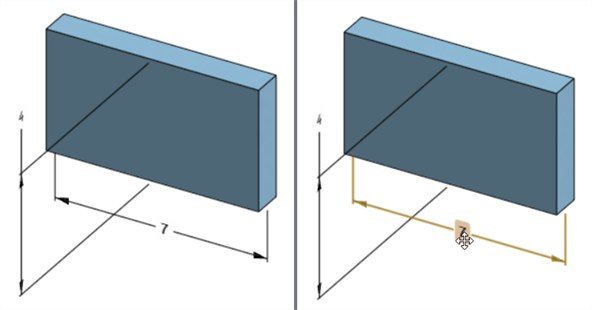
The Dimension context dialog opens with context placed on the dimension value. Simultaneously, the Sketch dialog opens:
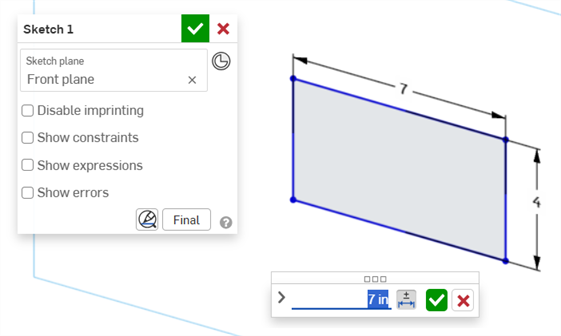
-
Using the keyboard, enter a numeric value or use the up/down arrows to increment the value in the Dimension context dialog. As this value is adjusted, the sketch is updated dynamically.
If entering a value numerically, press the tab key to see the sketch value update.
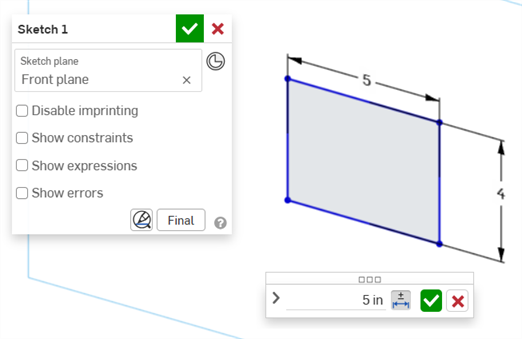
-
Press Enter on the keyboard or click the checkmark (
 ) in the Dimension context dialog to close this dialog:
) in the Dimension context dialog to close this dialog: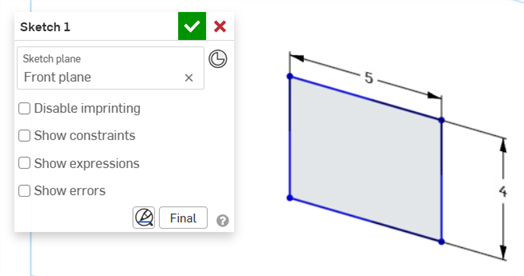
-
Press the checkmark (
 ) in the Sketch dialog to accept the new sketch value.
) in the Sketch dialog to accept the new sketch value.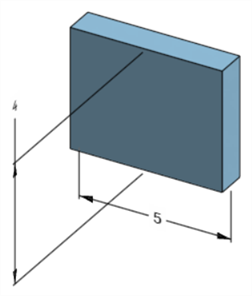
The edited sketch dimension that adjusts the model's dimension
-
Open the Inspection panel (
 ) to display the MBD dimensions in the graphics areas (left image below).
) to display the MBD dimensions in the graphics areas (left image below). -
Double-click on the driving dimension that is associated with a feature (right image below):
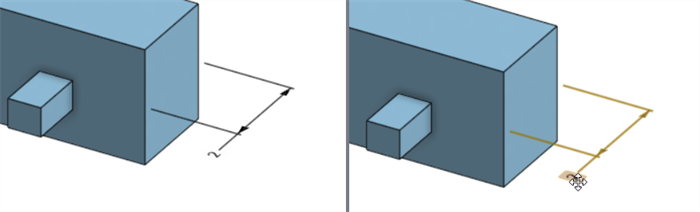
The Dimension context dialog opens with context placed on the dimension value. Simultaneously, the associated Feature dialog opens (Extrude in this example):
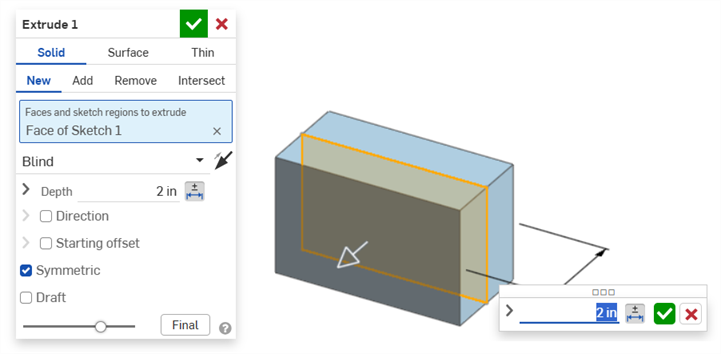
-
Using the keyboard, enter a numeric value or use the up/down arrows to increment the value in the Dimension context dialog. As this value is adjusted, both the model and the value in the Feature dialog are updated dynamically.
If entering a value numerically, press the tab key to see the value update in the Feature dialog.
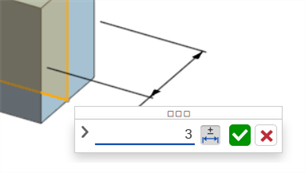
-
Press Enter on the keyboard or click the checkmark (
 ) in the Dimension context dialog to close this dialog:
) in the Dimension context dialog to close this dialog: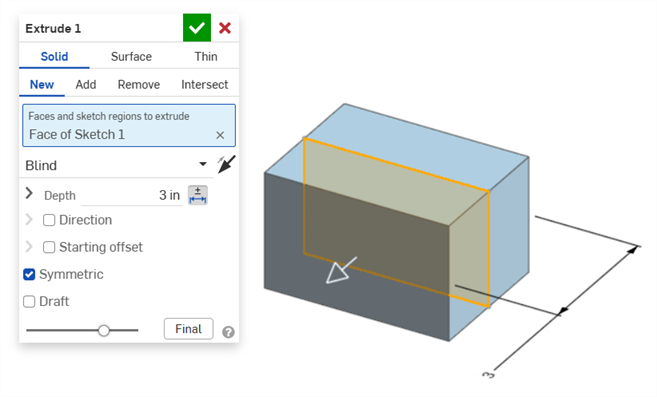
-
Press Enter on the keyboard again or click the Feature dialog checkmark (
 ) to close this dialog:
) to close this dialog:
The edited feature dimension that adjusts the model's dimension
To delete an annotation:
-
Select the annotation in the graphics area:
-
Press the Delete key.
-
The annotation is deleted from the graphics area and Inspection table.
If the annotation is a sketch or feature dimension:
-
The dimension's Tolerance options values are deleted.
-
The Tolerance options icon (
 ) is deselected.
) is deselected. -
The dimension value in the sketch or Feature dialog is not deleted.
-
Annotations cannot be deleted if:
-
The annotation is derived.
-
The annotation is created in a custom feature where the parameter is made tolerant but the tolerant toggle is not made available for user input.
In either case the following message is displayed:

-
Driven dimensions cannot be edited. Double-clicking on a driven dimension opens the Dimension context dialog, but values in the dialog cannot be edited.
-
Derived dimensions cannot be edited. Double-clicking on a driving or driven dimension from a derived part does not open the Dimension context dialog.
-
To cancel out of the Dimension context dialog, press the Esc key. If editing a feature dimension, the Dimension context dialog and Feature dialog close simultaneously. If editing a sketch dimension, only the Dimension context dialog closes. The sketch dialog must be manually closed (clicking the x icon).
-
Alternatively, with both the Feature dialog and Dimension context dialog open, the value in the Feature dialog can be selected and edited, which updates both the Dimension context dialog and model dynamically. Once edited here, pressing Enter closes both the Feature dialog and the Dimension context dialog simultaneously.
-
The location of the model dimension and location of its corresponding sketch dimension are not locked together. They are independent:
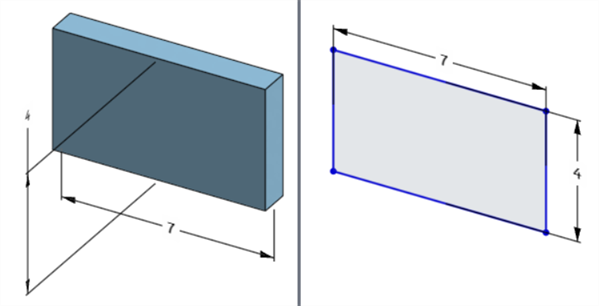
The model's width dimension is located below the model (left) but above the sketch (right)
-
In Pause regeneration mode, the model's dimension cannot be edited or deleted. However, you can still edit the feature or toggle a dimension's tolerance on or off. Changes take effect after clicking the Regenerate features and exit checkmark on the Paused regeneration banner.
-
Configurations work as expected. However, the dimension in the Dimension context dialog is not surrounded by a dashed orange outline to indicate it is configured. Configured sketch dimensions cannot be edited.
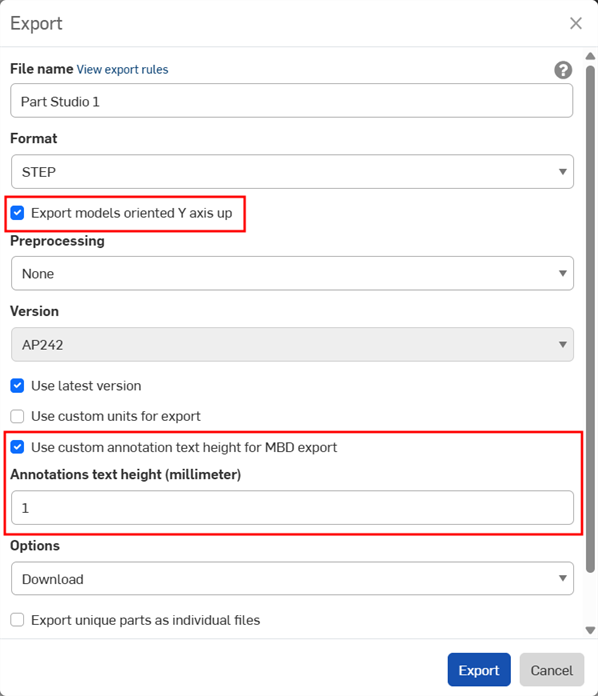
MBD data can be exported to STEP file format when exporting parts. The following settings are recommended:
MBD data is not exported with composite parts.
-
Enable the Export models oriented Y axis up checkbox.
-
Depending on the size of your model, you may need to enable the Use custom annotation text height for MBD export and select an appropriate Annotations text height to correspond to your model size.
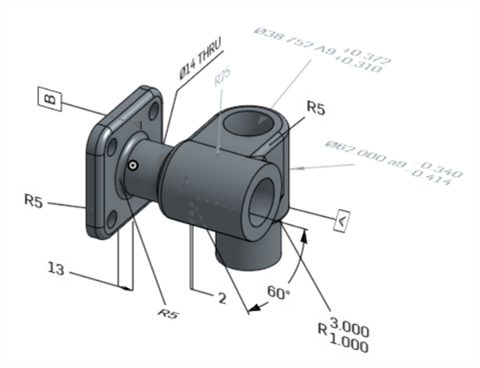
Original model in Onshape
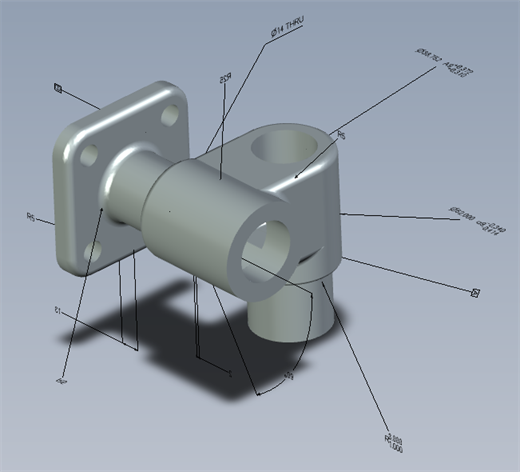
Exported model with the "Use custom annotation text height for MBD export" option disabled
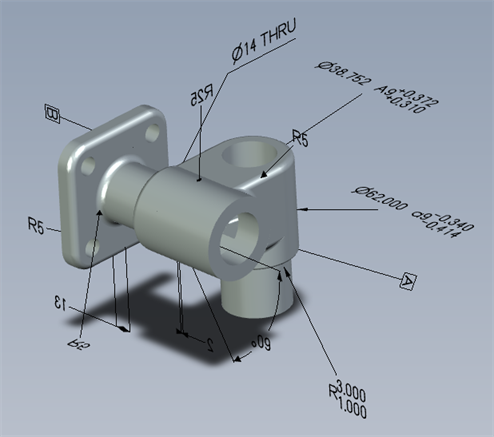
Exported model with the "Use custom annotation text height for MBD export" enabled and set to 10 mm.
When exported, Geometric tolerances with multiple Tolerance frames have Upper text combined with the top frame, and Lower text combined with the bottom frame.
The following provides MBD examples when working with Feature and dimension tolerances:
Depth dimension:
Offset distance dimension (with a composite part):
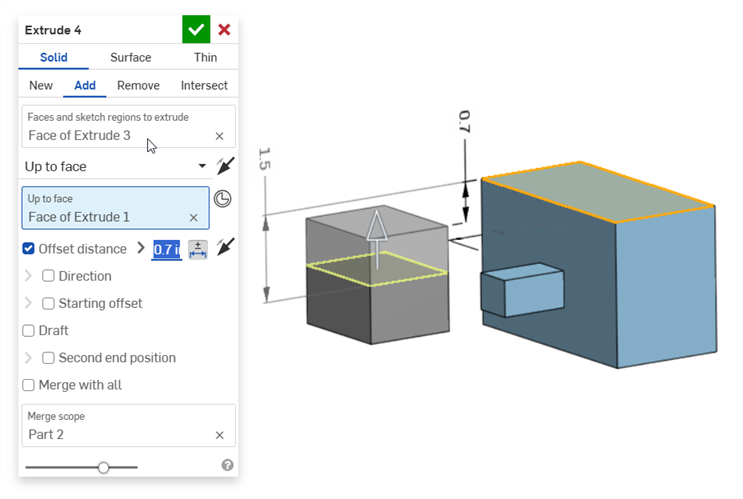
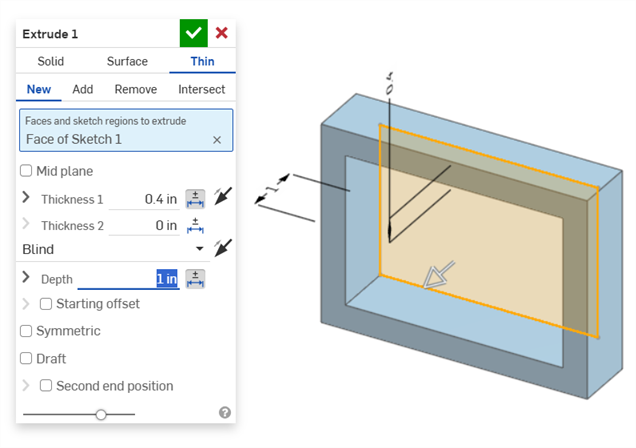
Thin extrude (Thickness 1 and Depth dimensions):
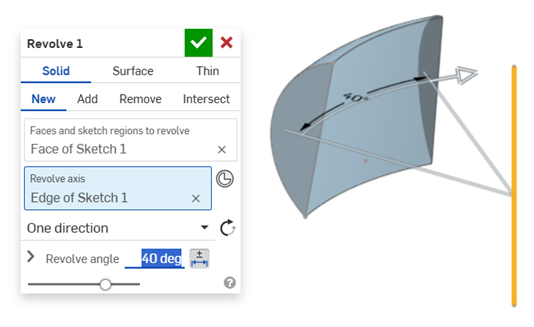
Revolve (Revolve angle dimension):
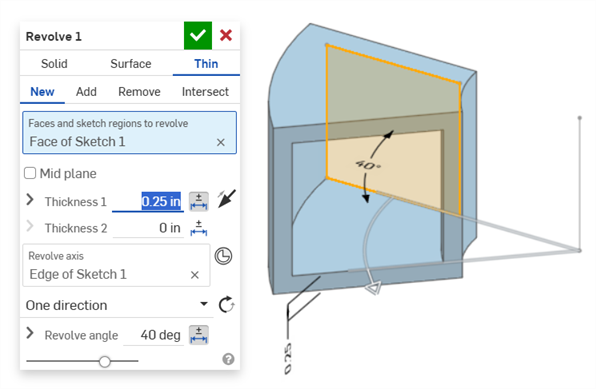
Revolve (Thickness 1 and Revolve angle dimensions):
Fillet (Radius dimension):
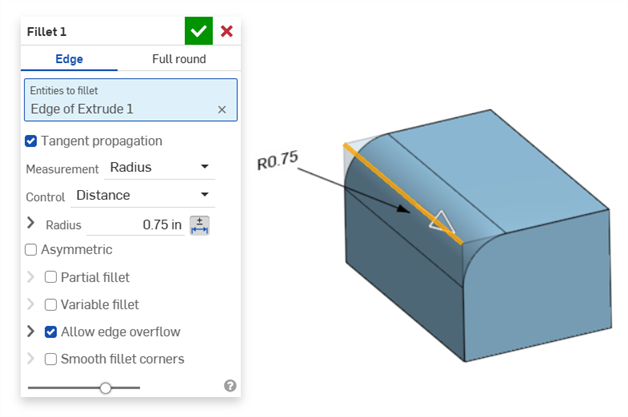
Creating a driven fillet dimension using the Inspection table's Fillet dimension tool on the Annotation toolbar:
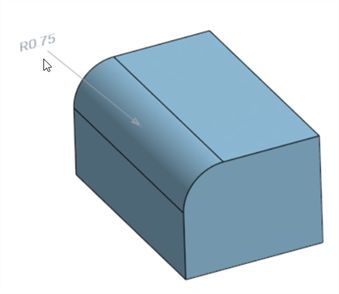
The Inspection panel's Dimension tool (![]() ) always uses linear or angular default tolerances. Dimensioning a filleted face using it applies a linear default tolerance type. For this reason, it is recommended to apply fillet tolerances from the Fillet feature dialog (for a driving dimension), or use the Fillet dimension from the Inspection panel (for a driven dimension).
) always uses linear or angular default tolerances. Dimensioning a filleted face using it applies a linear default tolerance type. For this reason, it is recommended to apply fillet tolerances from the Fillet feature dialog (for a driving dimension), or use the Fillet dimension from the Inspection panel (for a driven dimension).
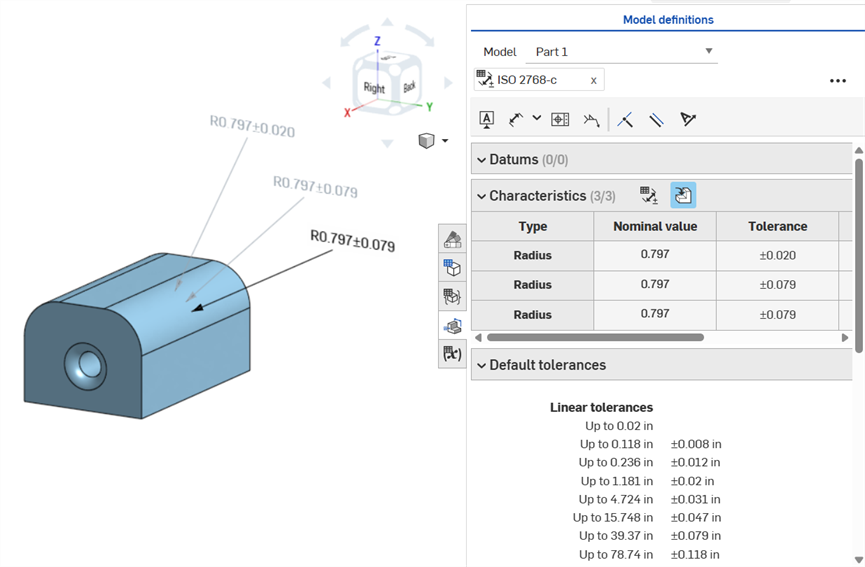
Dimensioning a fillet face: Annotated clockwise: Using the Dimension tool (driven; annotated in gray), using the Fillet dimension tool (driven; annotated in gray), and making the Fillet feature's Radius value tolerant (driving; annotated in black). All 3 dimensions are listed in the Characteristics table.
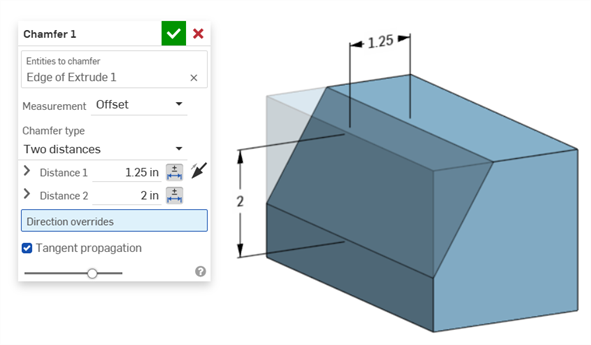
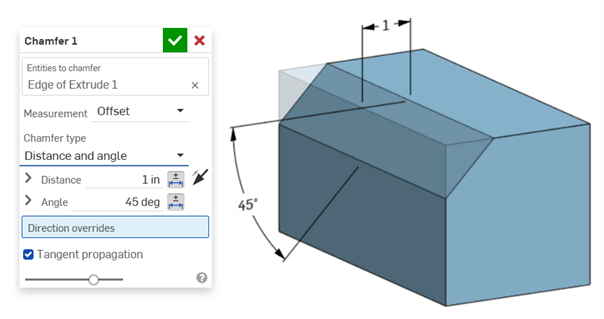
A Chamfer is defined as a distance to angle or distance to distance between a face and an edge. The Chamfer width dimensions are specified as the distance from an edge to the virtual sharp. The display for virtual sharps is added to the dimensioned edge, including a dashed curve.
-
Tolerances are not disabled When a tangent measurement is used, since they can work in certain cases, and especially when accounting for the specified tolerance.
-
In situations where two chamfer measurements are used (Two distances or Distance and angle), the user does not have to create tolerances for both. Tolerances can be added to only one parameter, if required.
Equal distance Chamfer type displays 2 Distance tolerance values, which are reflected in the table, even though there is only one distance tolerance option in the dialog:
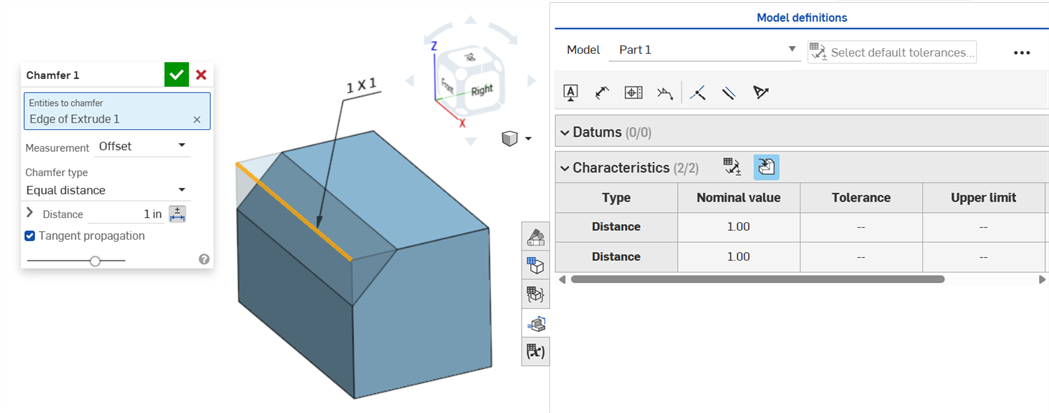
Two distances example:
Distance and angle example:
For cases where the chamfer results in a variable distance (for example, if the chamfer is applied to a cylinder face that is perpendicularly connected to another cylinder), try selecting tangent for the Measurement, to make the distance uniform along the edge:
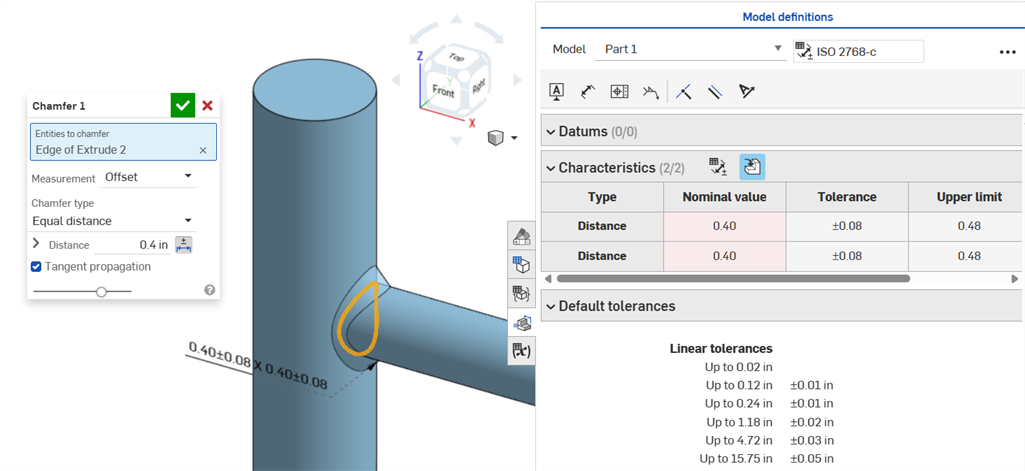
Non-uniform chamfer using an Offset measurement displaying a Nominal value error.
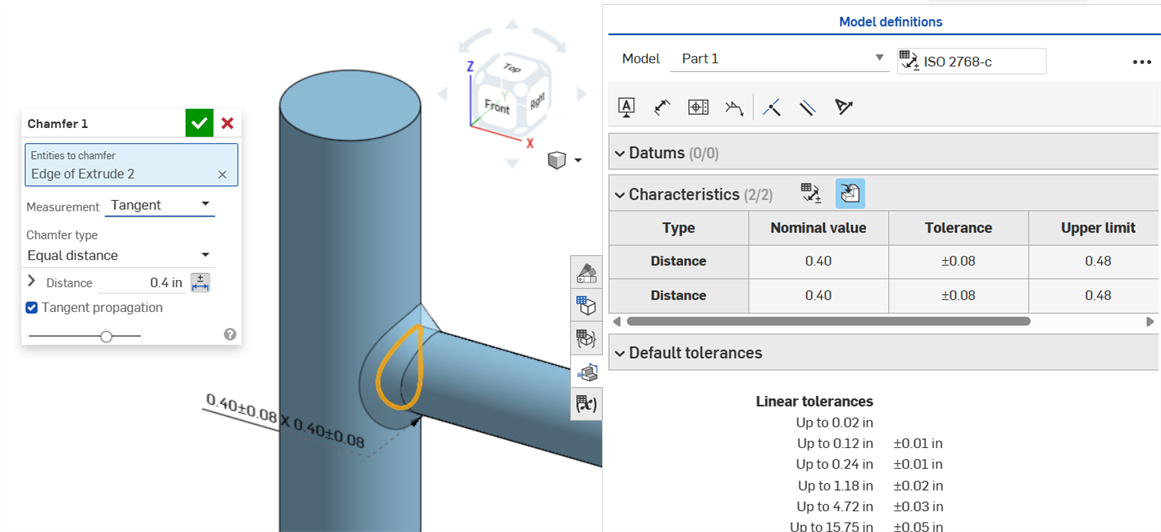
Uniform chamfer using a Tangent measurement results in a Nominal value without error.
If a tolerance is placed on a hole feature, it can be displayed in the Inspection table.
Some things to keep in mind:
-
Hole dimensions are only visible as rows in the Inspection table. There are no dimensions placed in the graphics area. This is done so as not to clutter the graphics area with callouts.
-
Before hole dimensions are visible in the Inspection table, another callout (a datum, for example) must be placed on the part.
-
Only one set of dimensions (Diameter, Distance, and/or Angle) are shown per hole feature. Patterned holes or additional holes in the same feature are not dimensioned separately.
-
The custom Tip angle dimension is not currently supported and does not create a row in the Inspection table.
-
Cross-highlighting works as follows:
-
Distance (Depth) is not cross-highlighted because there are no faces at either end of the hole, and edges are not currently supported for MBD.
-
Diameter, Distance (Counterbore depth), and Angle (Countersink angle) cross-highlights a single face.
-
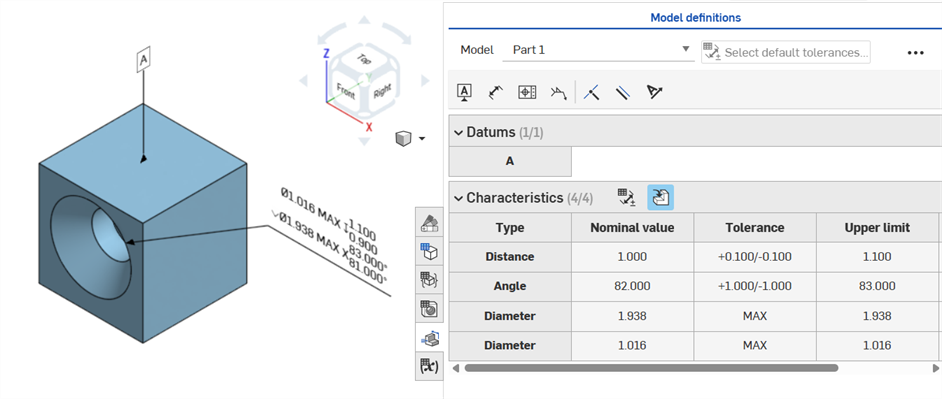
Hole dimensions are visible in the Inspection table after a Datum is added to one of the part's faces.
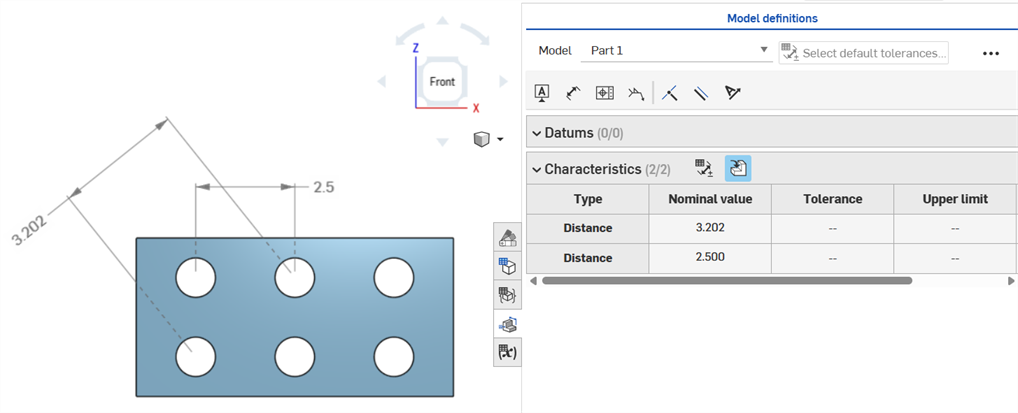
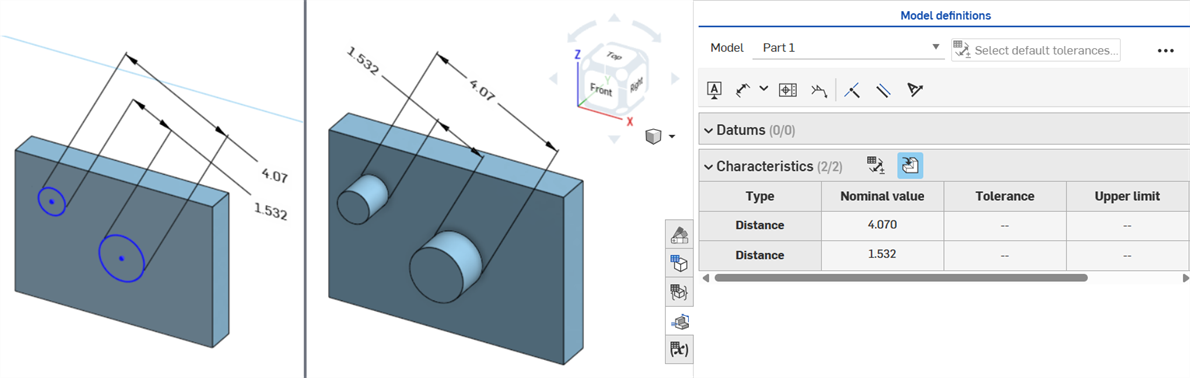
Axis distance dimensions between center circles using the Dimension (![]() ) tool:
) tool:
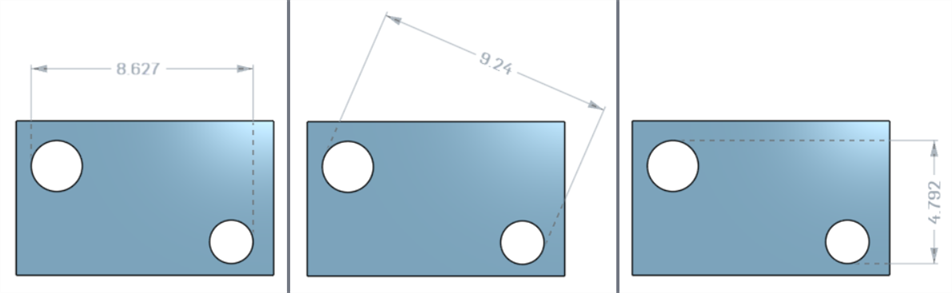
Minimum horizontal, diagonal, and vertical dimensions between two cylindrical faces using the Minimum dimension tool (![]() ):
):
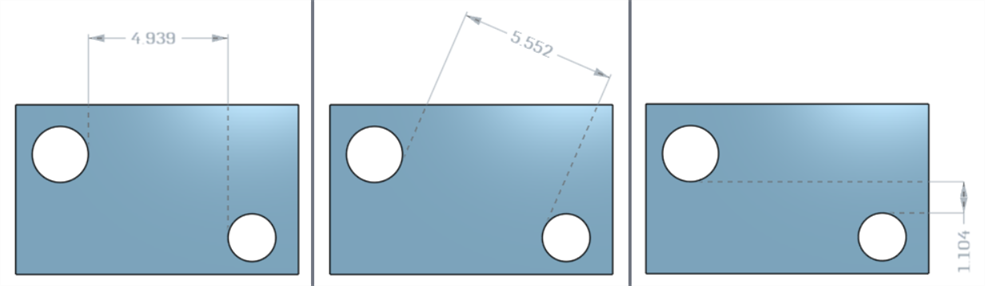
Minimum dimensions between cylinders and edges:
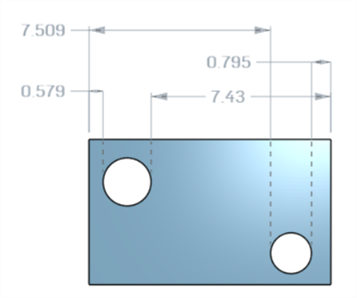
A minimum diagonal dimension added in a sketch (left) is displayed in the Characteristics table once the part is created (right):
Horizontal and vertical minimum dimensions cannot currently be created in a sketch.
Minimum horizontal, diagonal, and vertical dimensions between two cylindrical faces using the Maximum dimension tool (![]() ):
):
Maximum dimensions between cylinders and edges:
Maximum horizontal, diagonal, and vertical dimensions between arc faces in a slot:
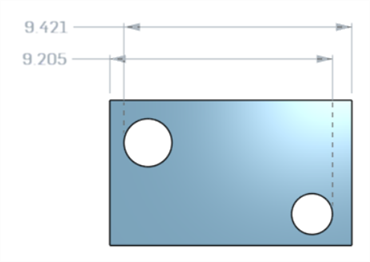
A maximum diagonal dimension added in a sketch (left) is displayed in the Characteristics table once the part is created (right):

Horizontal and vertical maximum dimensions cannot currently be created in a sketch.
Thickness is displayed in the Inspection table as a Distance row.
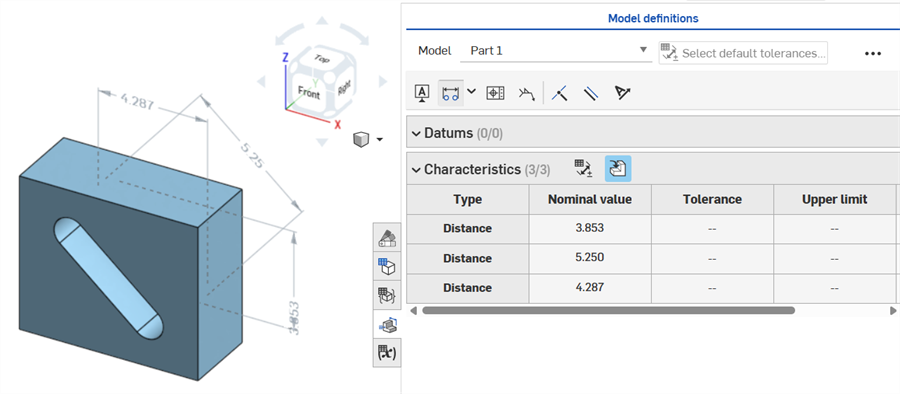
Thin extrude (Thickness 1 dimension):
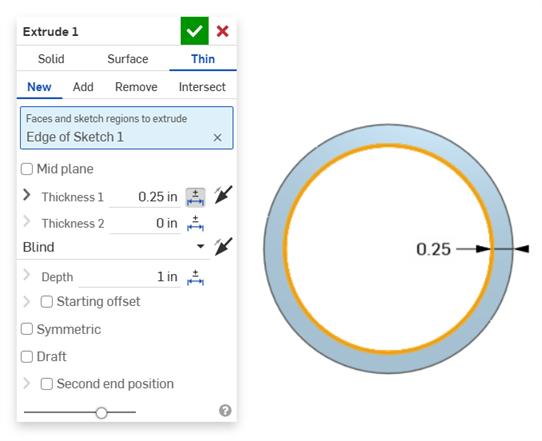
Thin revolve (Thickness 1 dimension):
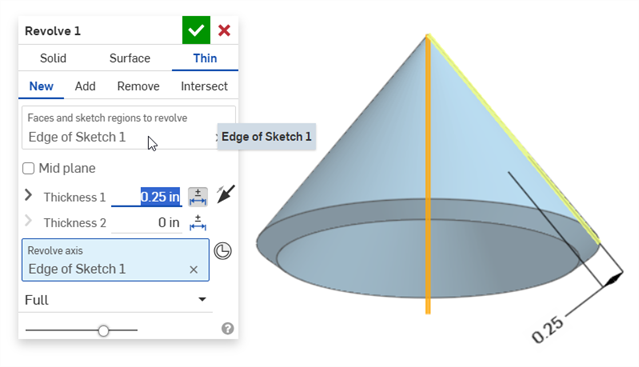
MBD errors do not create annotations or row entries in the Inspection table, unless an adjustment to the model is made that invalidates an existing annotation row entry.
Errors are displayed in red, similar to other Onshape errors:
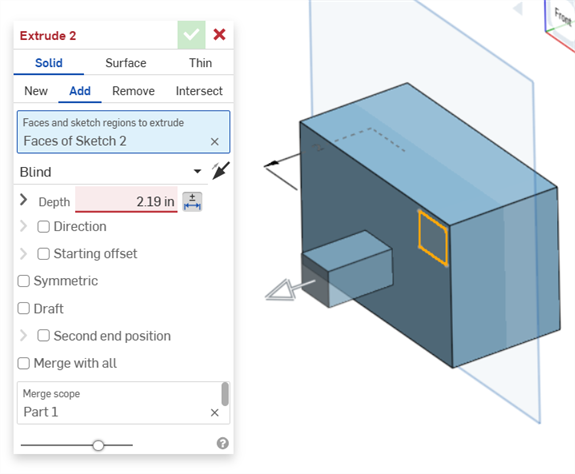
Error generated when extruding from or into a solid. The annotation does not generate a row entry in the Inspection table.
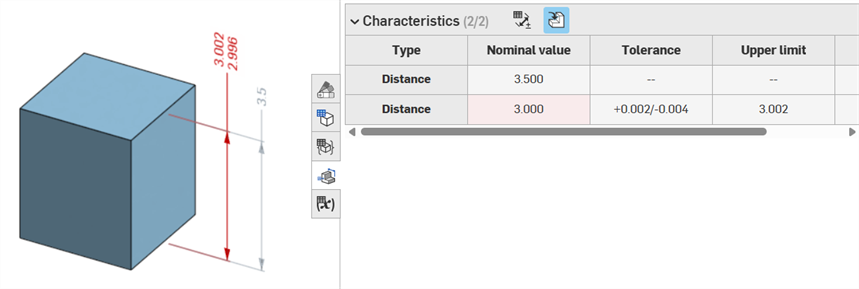
If the geometry is altered so as to invalidate a specified annotation, its corresponding annotation is red in the graphics area, and highlighted red in the Inspection table, signaling an error. For example, The top face of the box was moved .5 in., resulting in the measured value (3.5 in.) differing from the specified value (3.0 in.):
Error examples
-
A reference is missing for this annotation - Occurs when a reference is missing. For example, Part A is extruded up to the face of part B, and a tolerance is added to the Offset distance of the Part A extrusion.
-
Both faces must be from the same part - Model definitions are valid only on a per-part basis. For example, you cannot dimension the distance from a face on Part A to a face on Part B.
-
MBD annotations must always be associated with faces. Edges and vertices cannot currently be referenced.
-
Model definitions are valid only on a per-part basis. Composite parts are also valid. For example, you can dimension the distance between 2 faces on Part A or 2 faces on Part B, but not between a face on Part A and a face on Part B. To do this, first create a composite Part C from both Part A and Part B. You can then dimension the distance between these 2 faces.
-
Hovering over the Type row in the Inspection table cross-highlights the dimension in the graphics area.
-
When altering geometry of a part, all associated model definitions are highlighted orange:
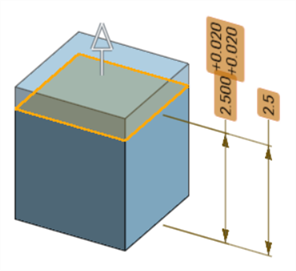
-
If a part or Part Studio is derived via the Derived feature, all model definitions are read-only and cannot be edited. You can still move annotations, and driven dimensions are still updated if the derived geometry is altered; however, the underlying model definitions can only be adjusted in the source Part Studio, and then updated in the Derived Feature. See Derived for more information.